西北高原所在青稞早熟适应性研究方面取得重要进展
青稞即裸大麦(Hordeum vulgare var. nudum),是青藏高原极具特色的作物类型,是藏民族农业文明的象征,它对青藏高原极端环境具有良好的适应性,是研究青藏高原短生育期条件下作物进化与适应的模式植物。研究青稞早熟性(early maturity)形成的遗传机制对于揭示青稞对青藏高原极短生育期条件的适应和进化过程具有重要的科学意义。同时,青稞早熟材料对提高青稞种植的海拔上限和增加复种指数具有重要的育种利用价值。
3月,国际农艺学顶级学术期刊Theoretical and Applied Genetics在线发表了中国科学院西北高原生物研究所麦类作物分子育种学科组和四川农业大学小麦研究所在青稞早熟适应性方面的最新研究成果:生物种基因EAM8 (EARLY MATURITY 8)内含子可变剪接可引起青藏高原青稞的早熟性和对短生育期的适应(Tengfei Xia, Lianquan Zhang, Jinqing Xu, Lei Wang, Baolong Liu, Ming Hao, Xi Chang, Tangwei Zhang, Shiming Li, Huaigang Zhang, Dengcai Liu*, and Yuhu Shen*. The alternative splicing of EAM8 contributes to early flowering and short-season adaptation in a landrace barley from the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2017, doi:10.1007/s00122-016-2848-2)(http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00122-016-2848-2)。
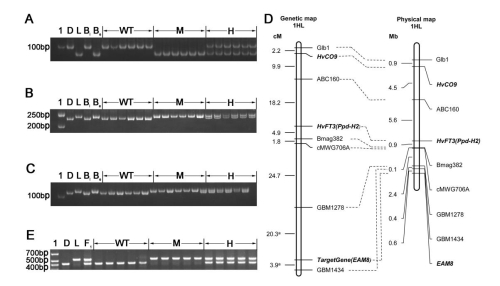
研究组在青海西宁和四川温江两地的表型鉴定结果发现,来自西藏的青稞地方品种“拉鲁青稞”开花时间比晚熟品种“迪青1号”早15-21天,生育期差异显著。通过对来自于拉鲁青稞(早熟)×迪青1号(晚熟)杂交组合的279个F2个体的表型分析,认为“拉鲁青稞”的早开花性状由单个隐性基因控制。进一步的遗传和物理图谱构建工作将该控制基因定位于1HL上并确定其为生物种基因(circadian clock genes)EAM8的隐性等位变异。亲本EAM8 的DNA和cDNA的序列分析结果表明,“拉鲁青稞”EAM8第三个内含子(intron 3)中存在的A/G替换导致该基因在转录时发生可变剪接(alternative splicing)和内含子保留(intron retention),之后提前出现的终止密码子最终导致无功能的截断蛋白(putative truncated protein)的形成,将该等位基因定名为eam8.l。在自然群体中的EAM8单体型(haplotype)检测结果表明,eam8.l存在于青藏高原野生大麦和青稞地方品种中且具有相同的早熟特性,推测该等位变异可能来自于西藏野生大麦。本研究发现的eam8.l等位基因是植物中第一个发现的可变剪接导致早熟的自然突变基因。本项研究结果不仅提示我们可变剪接可能是青稞生物钟基因进化和短生育期适应性形成的重要遗传机制之一,同时在青藏高原其它一年生植物中也可能存在相似的适应性形成机制。
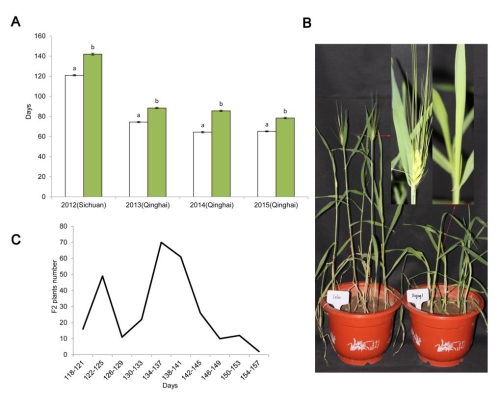
Fig. 1 Variation in the flowering time of Lalu and Diqing 1 plants grown in Sichuan and Qinghai. a Days to flowering (mean number of days to reach awn emergence on the leading tiller) of Lalu (white bars) and Diqing 1 (green bars). The error bars represent the standard error calculated from 19 Lalu plants and 13 Diqing 1 plants grown in Sichuan in 2012, and from 15 Lalu and 15 Diqing 1 plants grown in Qinghai in 2013-2015. b 60 day old plants of Lalu (left) and Diqing 1 (right). The arrows indicate the region of the leading tiller shown in magnified form. c The distribution of flowering time exhibited by the F2 progeny of the cross Lalu × Diqing 1.
Fig. 2 Mapping the gene underlying early flowering in Lalu. Amplicons obtained from the SSR assays a Bmag382, b GBM1278 and c GBM1434. d A genetic (left) and a physical (right) map of the region of chromosome arm 1HL where the gene was located. The genetic map incorporates loci mapped by Kikuchi et al. (2012). e Amplicons obtained from a PCR assay based on the primer pair EAM8-2822-F/EAM8-3235-R, which targets the 104 bp indel in intron 2. 1: Molecular weight marker, D: Diqing1, L: Lalu, Be: a DNA bulk prepared from 20 early flowering F2 segregants; Bl: a DNA bulk prepared from 20 late flowering F2 segregants, WT: homozygote for the Diqing 1 allele, M: homozygote for the Lalu allele, H: heterozygote, F1: Lalu × Diqing 1 F1 plant.



 青公网安备 63010402000197号
青公网安备 63010402000197号