“源于人工合成六倍体小麦的外源位点分布及功能注释”在《Plant Physiology and Biochemistry》杂志上发表
2018年6月28日,《Plant Physiology and Biochemistry》杂志在线发表了题为“The transfer to and functional annotation of alien alleles in advanced wheat lines derived from synthetic hexaploid wheat”的研究论文,该论文第一作者为我所曹东助理研究员,通讯作者为张怀刚研究员和刘宝龙研究员。
人工合成小麦与普通小麦的A、B、D染色体组同源,利用人工合成小麦为“桥梁”,与普通小麦优良品种(系)杂交,进一步用优良品种(系)回交和顶交,在改良人工合成小麦携带的不利性状的同时,可将位于人工合成小麦不同染色体位置的优良基因导入到普通小麦。利用人工合成小麦已培育了一批小麦新品种应用于小麦生产,如巴基斯坦的小麦新品种Lalma和KT-2010,墨西哥的Maravilla和西班牙的Carmona。在国内,利用源于CIMMYT的“硬粒小麦-节节麦人工合成小麦”,选育出了川麦38、川麦42、川麦43和川麦47等小麦新品种;利用中国圆锥小麦地方品种AS2255与中东节节麦AS60创制的人工合成小麦SHW-L1为材料,选育出“蜀麦969”等优良新品种。国内外育种实践证明,人工合成小麦有非常重要的育种价值,但其遗传机制尚不明确。
论文对经过田间选择的293份人工合成六倍体小麦SHW-L1改良新品系及其亲本进行了DArT全基因组扫描分析。结果表明,经过人工选择的人工合成六倍体小麦改良新品系都含有外源位点,但每个品系所含有的外源位点是不同的。组合SCPD、SS7M、SSYZ含有的外源位点分别为1824 (17.4%)个、1786 (17.1%)个、1514 (14.5%)。在3个组合的新品系中,组合SSYZ中有一个品系含有的外源位点百分率最低,为6.97%。组合SCPD中有一个品系含有外源位点的百分率最高,为30.41%。3个组合外源位点的的传递率介于0-100%;3个组合中传递率均为0的外源位点有44个,传递率为均为100%的外源位点有2个,与千粒重和抗叶锈相关。通过对外源位点注释发现,13个标记具有蛋白功能,与产量及其相关性状相关。该项研究证明外源位点存在于经过人工选择的改良品系中,且这些位点与小麦产量或抗病性等性状紧密相关。
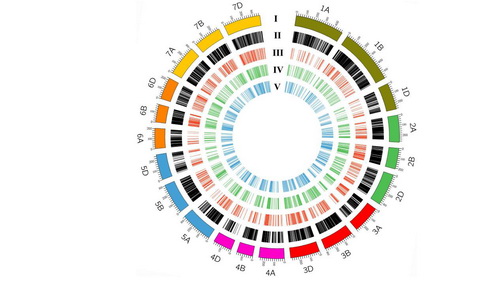
图1 284份SHW-L1改良品系DArT标记分布
注:圈I代表小麦21条染色体;圈II代表多态性DArT标记;圈III代表分布于组合SCPD中的外源位点;圈IV代表分布于组合SS7M中的外源位点;圈V代表分布于组合SSYZ中的外源位点。
ABSTRACT:The abundant genetic diversity in synthetic hexaploid wheat (SHW) can achieve breakthroughs in wheat genetic improvement, but little is known of the genetic mechanisms involved. In this study, three populations of advanced lines (totaling 284 individuals), derived from three top-crosses of SHW-L1 with different common wheat cultivars, followed by ten generations of artificial selection, were used to evaluate the transfer of alien alleles with 24872 Diversity Arrays Technology (DArT) markers. Only 1824, 1786 and 1514 DArT markers were needed to distinguish the alleles from SHW-L1 and the other common wheat parent in the populations SCPD, SS7M and SSYZ, respectively. The data clearly showed that all the advanced lines contained alien alleles from SHW-L1. The lowest percentage of alien alleles was 6.97% in an advanced line in population SSYZ, while the biggest was 30.41% in a SCPD advanced lines. The percentages of alien alleles at each locus ranged from 0% to 100% in all three populations. Forty-four alien alleles did not exist in all advanced lines, while two alien alleles were present in all advanced lines. Two of the 100% alien alleles were associated with thousand-grain weight and leaf rust resistance. Thirteen alien alleles were associated with grain yield, grain thickness and width, thousand-grain weight, grain weight/ear, plant height, grain weight, grain number, powdery mildew resistance, spikelet number per spike or yellow rust resistance. The research provided direct evidence of the existence of alien alleles in advanced lines and detected a number of valuable alleles related to wheat yield or disease resistance. More research is needed to analyze the functional mechanisms of these alleles, and to use these materials and alleles in wheat improvement.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.06.037



 青公网安备 63010402000197号
青公网安备 63010402000197号