“一种鉴别中国沙棘雌雄株性别的RAPD和SCAR分子标记”在《Molecules》杂志上发表
2018年5月1日,《Molecules》杂志在线发表了题为“Molecular Sex Identification in Dioecious Hippophae rhamnoides L. via RAPD and SCAR Markers”的研究论文,该论文第一作者为我所博士研究生周武,通讯作者为索有瑞研究员和胡娜助理研究员。该论文报道了一种用于中国沙棘雌雄性别鉴定的RAPD和SCAR分子标记。
中国沙棘Hippophae rhamnoides L. subsp. Sinensis Rousi属于胡颓子科Elaeagnaceae沙棘属Hippophae,是一种用途广泛的落叶灌木。沙棘果实虽味酸涩,但营养丰富的沙棘果汁富含维生素A、C、E、K和维生素P等多种维生素。此外,临床研究表明,沙棘果实能增强人体免疫功能,具有潜在的抗肿瘤活性,同时能防辐射,改善皮肤问题。然而,同大多数雌雄异株的多年生植物一样,沙棘的一个典型特征是,只有等到沙棘开花结果,否则无法鉴别沙棘幼苗的性别,而从沙棘幼苗到开花结果通常需要生长5~7年。如果在沙棘幼苗期就能根据某种标记辨别雌雄,就可以通过提高人工种植的沙棘园中沙棘雌株的比例来获得更高的果实产量和经济收益,同时只需要留下6%~7%的沙棘雄株来完成授粉。因此,需要开发一种有效和简便的方法来分辨中国沙棘幼苗的性别,从而使人工种植的沙棘园中保持一个最适的雌雄株比例。
论文以中国沙棘雌雄株叶片为试验材料,分别提取中国沙棘雌株和雄株DNA各140份,等量混合构建中国沙棘雌雄株DNA混池。为了提高通过RAPD扩增筛选能扩增出性别差异性条带的效率和可靠性,本论文基于优化的RAPD-PCR反应体系,通过筛选得到中国沙棘性别相关特异性条带,并转化为可靠的SCAR分子标记。该SCAR分子标记能在140株雌性个体中扩增出885 bp的特异性片段,而所有的中国沙棘雄性中均未出现,因此能准确地将中国沙棘雌株从中国沙棘雄株中鉴别出来。
Abstract:The dioecious property of the sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) prevents sex recognition via traditional observation at the juvenile stage, thus impeding breeding and economic cropping; A random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and a sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) markers were used to identify the sexes. A total of 45 random decamer primers were used to screen genomic DNA pools of staminate and pistillate genotypes for genetic polymorphisms. One female sex-linked marker was identified. D15 (5′-CATCCGTGCT-3′) amplified a particular band of 885 bp, which showed polymorphism among staminate and pistillate genotype plants. The SCAR marker Hrcx-15 was obtained by sequencing the fragment. The alleles of 140 pistillate genotypes were examined but not of the 140 staminate genotypes discerned via taxonomy. Staminate and pistillate genotypes of sea buckthorn plants can be distinguished, using Hrcx-15 as a genetic marker for sex identification and for expediting cultivation for commercial applications.
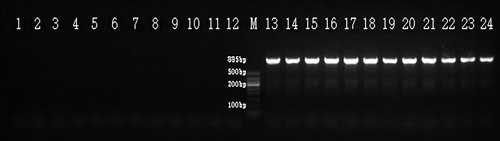
图1 SCAR分子标记在中国沙棘雄株和雌株中的部分扩增结果
注:1-12:中国沙棘雄株,13-24:中国沙棘雌株。M,DNA Marker DL500 (Takara,大连宝生物)。



 青公网安备 63010402000197号
青公网安备 63010402000197号